Orbit is designed to explore network of a blockchain wallet by recursively crawling through transaction history.
The data is rendered as a graph to reveal major sources, sinks and suspicious connections.
Usage
Let’s start by crawling transaction history of a wallet
python3 orbit.py -s 1AJbsFZ64EpEfS5UAjAfcUG8pH8Jn3rnOfCrawling multiple wallets is no different.
python3 orbit.py -s 1AJbsFZ64EpEfS5UAjAfcUG8pH8Jn3rn1F,1ETBbsHPvbydW7hGWXXKXZ3pxVh3VFoMaXOrbit fetches last 50 transactions from each wallet by default, but it can be tuned with -l option.
python3 orbit.py -s 1AJbsFZ64EpEfS5UAjAfcUG8pH8Jn3rn1F -l 100 Orbit’s default crawling depth is 3 i.e. it fetches the history of target wallet(s), crawls the newly found wallets and then crawls the wallets in the result again. The crawling depth can be increased or decresead with -d option.
python3 orbit.py -s 1AJbsFZ64EpEfS5UAjAfcUG8pH8Jn3rn1F -d 2 Wallets that have made just a couple of interactions with our target may not be important, Orbit can be told to crawl top N wallets at each level by using the -t option.
python3 orbit.py -s 1AJbsFZ64EpEfS5UAjAfcUG8pH8Jn3rn1F -t 20 If you want to use the collected data in some other way, you can save it to a JSON file by using the o option as follows
python3 orbit.py -s 1AJbsFZ64EpEfS5UAjAfcUG8pH8Jn3rn1F -o output.jsonVisualization
Once the scan is complete, the graph will automatically open in your default browser. If it doesn’t open, open quark.html manually. Don’t worry if your graph looks messy like the one below or worse.
Read More: Top 5 Technology Trends For 2019
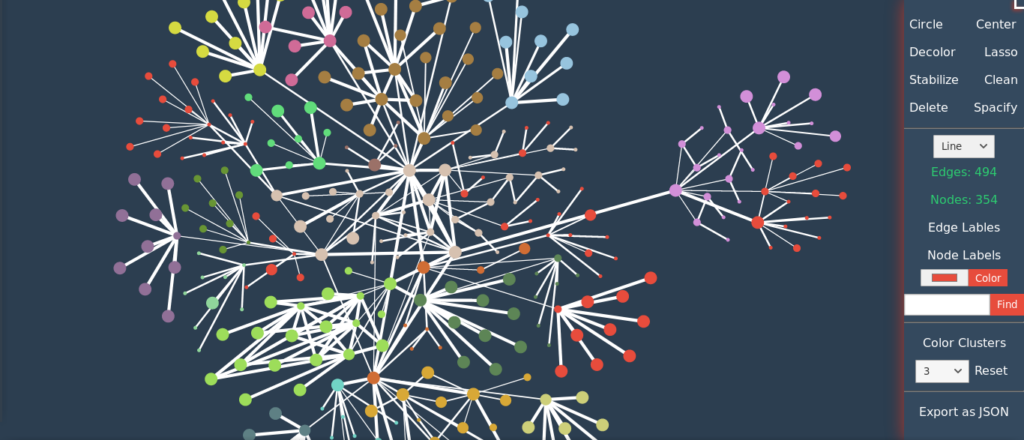
Select the Make Clusters option to form clusters using community detection algorithm. After that, you can use Color Clusters to give different colors to each community and then use Spacify option to fix overlapping nodes & edges.
Read More: Trape: Easily Track People On Internet
As Orbit uses Quark to render the graph, more information about the various features and controls is available in Quark’s README.



