The data in the network layer is called datagrams. IPv4 does fragmentation for the datagrams. Each fragment is called a packet.
The reason of fragmentation is to send a large size data (datagrams) through a link with a limited MTU (maximum transmission unit, usually 1500 Byte).
In an IP packet/datagram, the header contains the addressing information, such as the sender’s source and the destination’s IP address. An IP packet is usually unencrypted, therefore if someone is sniffing the traffic between the sender and the receiver, the contents of the packet and its header information are captured.
A malicious user or an attacker can modify the IP address on the IP packets originating from the attacker machine, making it seem to originate from somewhere else, which is known as IP spoofing. It tricks a potential victim into believing the IP packet came from a legitimate or trusted source, but is actually from a malicious user. The operating system has no way of determining whether the IP addresses actually belong to the legitimate machine or not.
When the internet protocol was built, security was not a concern at the time, hence IP lacks security features.
There are different types of spoofing attacks:
- Address Resolution Protocol spoofing
- DNS spoofing
IP spoofing
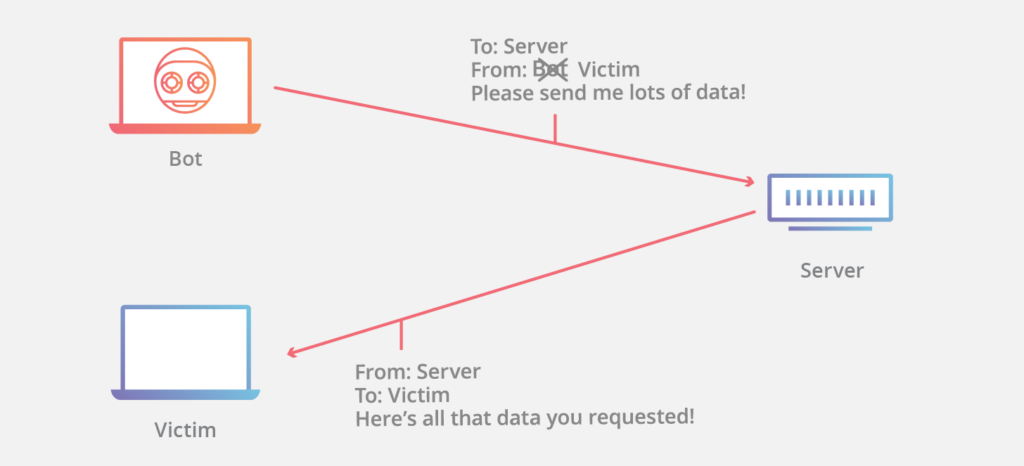
Using the following scenario, an attacker sends a specially crafted packet to the web server (200.1.1.1). Within the IP header of the specially crafted packet, it has a source IP address of 203.155.182.1, which belongs to the potential victim machine and not the real IP address of the attacker.
When the web server receives the packet and has to respond, it sees the sender’s IP address is 203.155.182.1 and sends its response to the victim machine instead of the attacker:
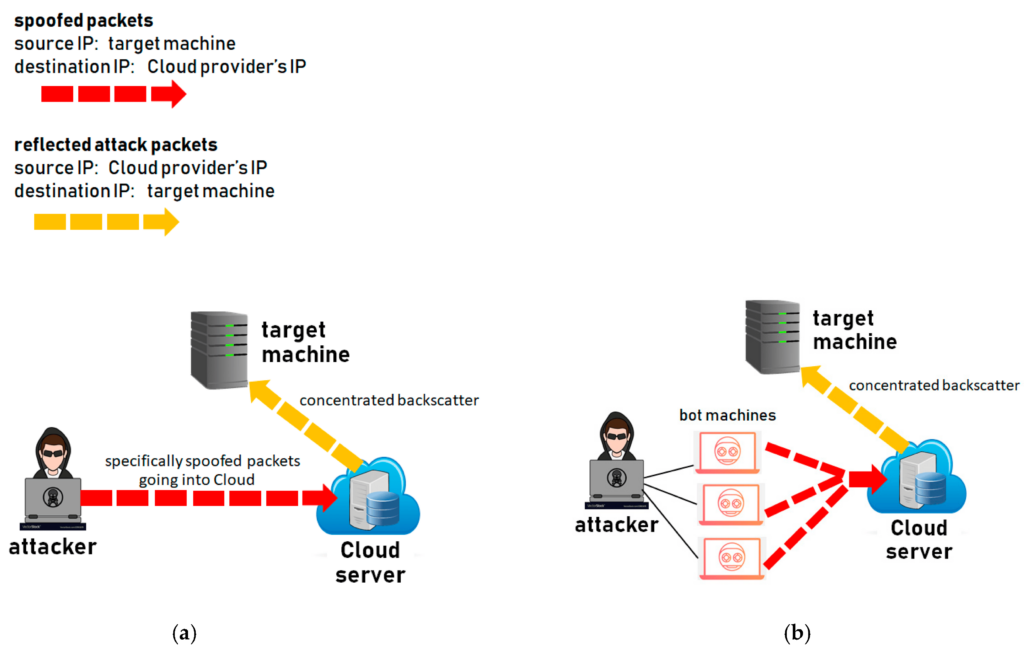
Attackers primarily use IP spoofing as a technique to bypass any filters, access lists, or even security appliances that act as countermeasures for spoofing attacks. The goal is to find a way into a network by tricking the system into believing it’s a legit packet.
In this method, the attacker creates IP packets with a fake source IP address to hide the identity of the sender. Attackers use IP spoofing to overcome security measures, such as authentication-based IP networks. Attackers use randomly chosen IP address and spoof the original IP address to perform the DoS attack.
Read Also: Private Internet Access – Most Popular VPN With No Traffic Logs
When two computers communicate, information about the IP address is placed on the source field of the packet. In an IP spoofing attack, the source IP address in the packet is not the original IP address of the source computer.
By modifying the source IP address, the original sender can make the victim machine think the message originated from another source and therefore the sending machine or the attacker will be protected from being tracked.
Various options where IP spoofing can be used:
- Scanning
- Hijacking an online session
- Flooding



